When asked to describe 2021 in one word, we may all have different views on the year that’s nearing its end. But we can probably agree that the past 12 months have been turbulent with political standoffs, a roller-coaster ride of a pandemic, and an economy trying to recover. As we’re nearing the end of 2021, let’s look back at some of its main events.
January 20: Joe Biden is inaugurated as the 46th president of the United States with Kamala Harris as Vice President.
February 2: The Fed ups its rhetoric, trying to keep the country calm through copious amounts of money printing.
February 7: Tom Brady wins the Super Bowl at age 43, his seventh Super Bowl victory.

February 10: The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reports that inflation for the year ending in January was 1.4%.
February 13-17: Winter storm Uri decimates parts of North America, Texas being hit especially hard.
March 10: The latest inflation data from the BLS shows inflation increased to 1.7% in February, the biggest annual gain in a year.
March 11: Biden signs the $1.9 trillion coronavirus relief package, which includes direct payments of up to $1,400 and an extension of a $300 per week unemployment insurance supplement.
March 22: The Biden administration proposes a $3 trillion spending package for economic recovery.
March 23-29: Massive cargo ship Ever Given gets stuck in Suez Canal.

April 13: Inflation climbs to 2.5% for the year ending in March.
April 28: Fed Chair Jerome Powell calls inflation “transitory.”
May 5: SpaceX successfully recovers Starship prototype for the first time.
May 7: A dismal jobs report launches Biden’s push for the American Jobs Plan and American Families Plan (a $4 trillion proposal)
Mary 10: Chicago Federal Reserve President Charles Evans says that 2.5% inflation doesn’t bother him “as long as it’s consistent with averaging 2% over some period of time.”
May 12: The annual inflation rate for April comes in at 4.2%, the sharpest increase in over 12 years. It beats economists forecast of 3.6%.
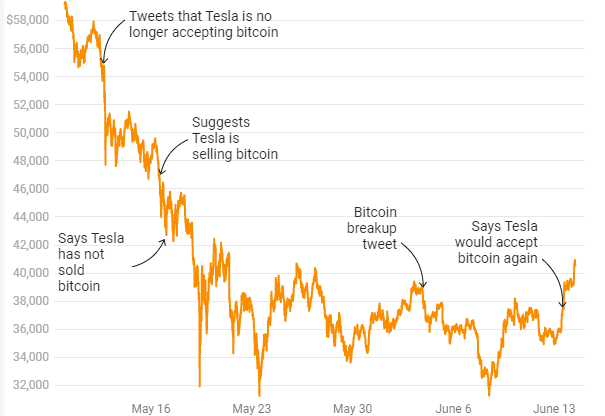
May 12: Tesla suspends vehicle purchases using Bitcoin. Shortly after, the cryptocurrency drops 15%.
June 10: Inflation reaches 5%, beating Wall Street expectations.
June 22: Powell reiterates that he views inflation as temporary and says it’s “very, very unlikely” the US will see 1970s-style inflation.
July 8: Biden is asked if he sees any parallels between the withdrawals from Vietnam and Afghanistan. He responds: “There’s going to be no circumstance where you see people being lifted off the roof of an embassy of the United States from Afghanistan. It is not at all comparable.”
July 11: Richard Branson flies into space on his rocket ship.
July 13: Inflation for the year ending in June jumps to 5.4%.
July 20: Jeff Bezos completes an 11-minute trip to space and back aboard the rocket and capsule system developed by his space company, Blue Origin.

July 28: Jerome Powell says the Fed expects inflation to remain above the objective before he expects it to move back down.
August 8: Tokyo’s “2020” Olympics (held this year in 2021) ends with USA taking home more gold medals than any other country (39 golds) beating China by 1 (38 golds).
August 15: The US evacuates diplomats by helicopter from its embassy in Kabul, Afghanistan.
August 30: The last US military forces leave Afghanistan, ending the nearly 20-year-long conflict.

September 7: El Salvador recognizes Bitcoin as a legal tender.
October 28: The US economy grew at a 2% annualized pace in the third quarter, its slowest increase since the end of the 2020 recession.
November 3: The Fed starts tapering its easy-money policies and reduces its $120 billion/month bond-buying by $15 billion.
November 10: Inflation accelerates to 6.2%. Biden says that reversing inflation is a “top priority” while urging lawmakers to pass his $3 trillion Build Back Better agenda.
November 15: Biden signs his $1.2 trillion infrastructure bill into law.
November 30: Jerome Powell on calling inflation “transitory”: “I think it’s probably a good time to retire that word.” He adds that “factors pushing inflation upward will linger well into next year.”
December 1: The first case of the Omicron Coronavirus variant is reported in the US.
December 2: Treasury Secretary on calling inflation “transitory”: “I am ready to retire the word transitory. I can agree that that hasn’t been an apt description of what we are dealing with.”
December 10: The consumer price index rises to 6.8%, the highest in four decades. A Congressional Budget Office analysis of the Build Back Better plan estimates that it would “increase the deficit by $3 trillion over 2022 to 2031” if a series of provisions were extended long term.
December 13: Allianz Chief Economic Advisor Mohamed El-Erian: “The characterization of inflation as transitory is probably the worst inflation call in the history of the Federal Reserve, and it results in a high probability of a policy mistake.”
December 15: The Fed announces it will accelerate its tapering and end its bond purchases in March 2022. It also signals that it will raise interest rates as many as three times in 2022.

December 20: Goldman Sachs reduces its forecast for the US economy from 3% to 2% for the first quarter of 2022.
December 28: The Buffett Indicator, which measures the value of the stock market to GDP, reaches a record high of 210.2, which means the stock market is “significantly overvalued.”
The post 2021 Year in Review: A timeline of events, policies, and a big boat that got stuck. appeared first on Gold Alliance.